Tornado Cash deposits linked to $282M wallet compromise in alarming CertiK investigation
Blockchain security firm CertiK has uncovered a sophisticated money laundering operation connecting $63 million in Tornado Cash deposits to the devastating $282 million cryptocurrency wallet compromise that occurred on January 10, 2025. This revelation exposes the intricate methods attackers employ to obscure stolen funds, significantly complicating recovery efforts for victims and investigators alike. The findings highlight growing concerns about cryptocurrency security and the challenges of tracking assets once they enter privacy-focused protocols.
Tornado Cash deposits reveal sophisticated laundering path
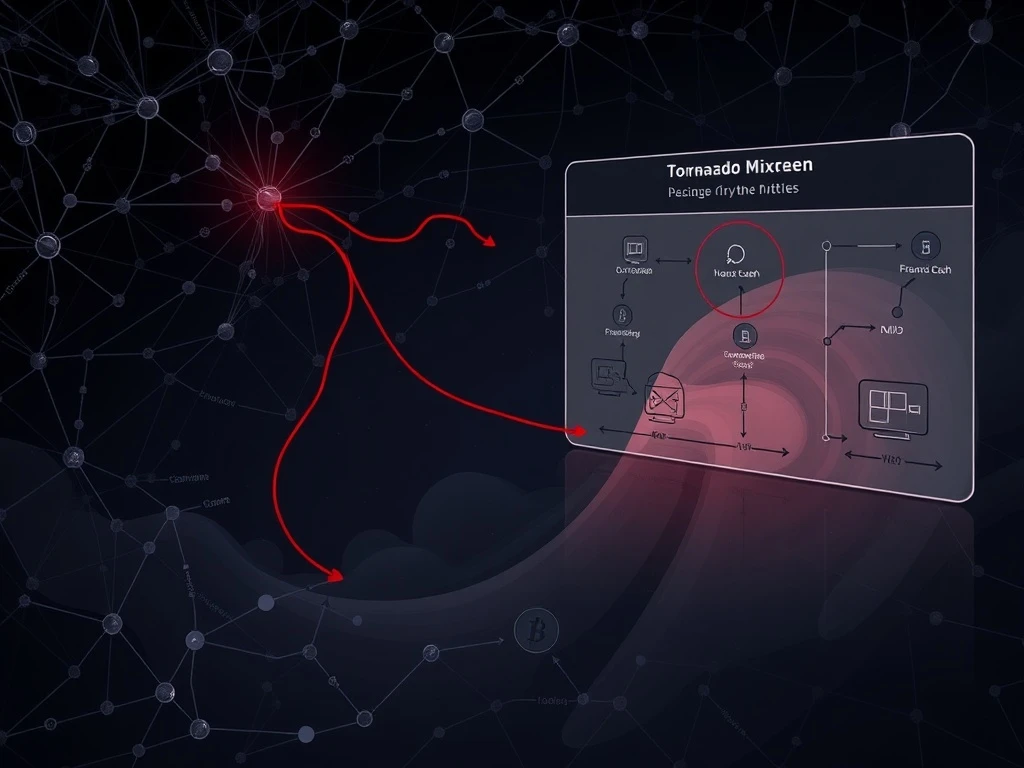
CertiK’s monitoring systems identified specific Tornado Cash interactions directly tied to the January 10 exploit, providing crucial insights into post-theft money laundering mechanics. According to their detailed analysis, the attacker employed a multi-stage process designed to erase the digital trail of stolen assets. Initially, the criminal bridged stolen Bitcoin to the Ethereum network using cross-chain swap technology.
This strategic move converted approximately 686 Bitcoin into 19,600 Ether, consolidating the funds into a single Ethereum address. Subsequently, the attacker fragmented these assets across multiple wallets, creating a complex web of transactions. Each address received several hundred Ether before routing the funds into Tornado Cash, the privacy-focused mixing protocol that effectively obscures transaction histories.
The laundering operation demonstrates several key characteristics:
- Cross-chain movement: Converting Bitcoin to Ether to leverage Ethereum’s extensive DeFi ecosystem
- Fragmentation strategy: Splitting large amounts into smaller, less conspicuous chunks
- Timing optimization: Executing transactions during periods of high network activity
- Protocol selection: Choosing Tornado Cash specifically for its privacy guarantees
Blockchain forensic analysis uncovers laundering patterns
CertiK’s investigation reveals that the $63 million represents only a portion of the total $282 million stolen during the January 10 incident. However, this specific money laundering pathway provides valuable intelligence about contemporary cryptocurrency theft methodologies. The security firm’s diagram maps the complete laundering journey, showing how attackers systematically obscure fund origins.
Marwan Hachem, CEO of blockchain security firm FearsOff, confirms that this flow follows established laundering patterns. “This operation mirrors the classic large-scale laundering playbook, particularly for cross-chain thefts involving Bitcoin and Litecoin,” Hachem explained. He noted that using THORswap for Bitcoin-to-Ether conversions and breaking funds into approximately 400 ETH chunks before entering the mixer represents “textbook” obfuscation techniques.
These methods serve dual purposes: reducing attention from monitoring systems and making post-mixing recovery substantially more difficult. The strategic approach demonstrates sophisticated understanding of blockchain forensics and anti-tracking measures employed by security firms.
Expert analysis of recovery challenges
Hachem emphasized the significant challenges facing recovery efforts after funds enter mixing protocols. “Tornado Cash functions as a major kill switch for traceability,” he stated, adding that recovery chances “drop to near zero” in most cases following mixer deposits. This reality presents substantial obstacles for victims seeking to reclaim stolen assets.
The limitations become particularly apparent when examining mitigation options available after mixer interactions. According to Hachem, these options remain “limited and increasingly unreliable” as mixing technology evolves. This assessment underscores the critical importance of preventive security measures and rapid response protocols following cryptocurrency thefts.
Social engineering attack enables massive compromise
The January 10 theft originated from a sophisticated social engineering attack that manipulated the victim into revealing a seed phrase. As previously reported by blockchain investigators, the attacker impersonated wallet support staff, gaining complete control over the victim’s cryptocurrency holdings. This compromise affected a wallet containing approximately 1,459 Bitcoin and over 2 million Litecoin.
Blockchain investigator ZachXBT documented how the impersonation technique allowed the attacker to bypass traditional security measures. The social engineering approach highlights evolving threats in cryptocurrency security, where technical protections can be undermined through psychological manipulation.
Additional investigation revealed that portions of the stolen assets were converted into privacy-focused digital currencies, further complicating tracking efforts. Security firm ZeroShadow previously identified approximately $700,000 of stolen funds that were flagged and frozen early in the laundering process. However, the overwhelming majority of assets successfully moved beyond reach, demonstrating the effectiveness of the attacker’s methodology.
Comparative analysis of cryptocurrency laundering techniques
The January 10 incident provides valuable data for understanding evolving cryptocurrency laundering patterns. When compared to previous major thefts, several trends emerge regarding attacker behavior and security response capabilities.
| Laundering Technique | Frequency in Major Thefts | Effectiveness Rating | Common Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-chain bridging | High (85%+) | Very Effective | Cross-chain monitoring tools |
| Fund fragmentation | Extremely High (95%+) | Highly Effective | Pattern recognition algorithms |
| Mixer utilization | Moderate (60%) | Extremely Effective | Limited legal/technical options |
| Privacy coin conversion | Increasing (45%) | Very Effective | Exchange cooperation required |
This comparative analysis reveals that attackers increasingly combine multiple techniques to maximize obfuscation. The January 10 operation employed three of the four primary methods, demonstrating comprehensive understanding of anti-forensic measures.
Industry implications and security recommendations
The CertiK findings carry significant implications for cryptocurrency security practices across multiple sectors. Exchange platforms, wallet providers, and institutional investors must reassess their security protocols in light of these sophisticated laundering techniques. The incident particularly highlights vulnerabilities in social engineering defenses and the critical need for enhanced user education.
Security experts recommend several protective measures based on this investigation:
- Multi-signature wallets: Implementing additional transaction approval requirements
- Behavioral monitoring: Deploying systems that detect unusual fund movement patterns
- Enhanced verification: Establishing stricter protocols for support interactions
- Rapid response plans: Developing procedures for immediate action following detected compromises
These recommendations address both technical vulnerabilities and human factor risks identified in the January 10 incident. Implementation requires coordinated efforts across the cryptocurrency ecosystem, including exchanges, wallet developers, and security providers.
Regulatory considerations and compliance challenges
The sophisticated laundering operation uncovered by CertiK presents substantial challenges for regulatory compliance and enforcement. Privacy protocols like Tornado Cash create complex legal and technical dilemmas for authorities attempting to track illicit funds. These challenges become particularly pronounced in cross-jurisdictional investigations involving multiple legal frameworks.
Recent regulatory developments have attempted to address these issues through enhanced reporting requirements and international cooperation frameworks. However, the technical sophistication demonstrated in the January 10 incident suggests that regulatory measures must evolve alongside technological advancements. This evolution requires ongoing dialogue between regulators, technology developers, and security experts.
Conclusion
CertiK’s investigation linking $63 million in Tornado Cash deposits to the $282 million wallet compromise reveals the sophisticated methodologies employed by contemporary cryptocurrency attackers. The multi-stage laundering operation, combining cross-chain transfers, fund fragmentation, and mixer utilization, demonstrates comprehensive understanding of blockchain forensics and anti-tracking measures. These findings underscore the critical importance of enhanced security protocols, user education, and rapid response capabilities within the cryptocurrency ecosystem. As laundering techniques continue evolving, security firms, exchanges, and regulators must develop corresponding advancements in detection and prevention methodologies to protect digital assets effectively.
FAQs
Q1: What is Tornado Cash and how does it relate to cryptocurrency laundering?
Tornado Cash represents a privacy-focused Ethereum mixing service that obscures transaction histories by pooling funds from multiple users. Attackers frequently utilize this protocol to complicate tracking efforts following cryptocurrency thefts, as demonstrated in the January 10 wallet compromise investigation.
Q2: How did CertiK link the Tornado Cash deposits to the specific wallet compromise?
CertiK employed advanced blockchain monitoring systems that identified transaction patterns connecting Tornado Cash interactions to the January 10 theft. Their analysis traced the laundering path from initial Bitcoin conversion through Ethereum bridging to final mixer deposits.
Q3: What makes recovery so difficult after funds enter mixing protocols?
Mixing protocols like Tornado Cash effectively break the transparent chain of custody that characterizes most blockchain transactions. This obfuscation creates substantial technical and legal challenges for investigators attempting to trace stolen funds through the mixing process.
Q4: How common are social engineering attacks in major cryptocurrency thefts?
Social engineering represents a growing threat vector in cryptocurrency security, with approximately 35% of major thefts involving some form of psychological manipulation. The January 10 incident demonstrates how sophisticated impersonation techniques can bypass technical security measures.
Q5: What security measures can individuals implement to protect against similar attacks?
Individuals should employ multi-signature wallets, enable transaction confirmation delays, verify all support communications through official channels, and utilize hardware wallets for significant holdings. Regular security education remains crucial for recognizing evolving social engineering tactics.