Google Play Crypto Ban: South Korea’s Regulatory Crackdown Creates Critical Hurdles for Binance and OKX
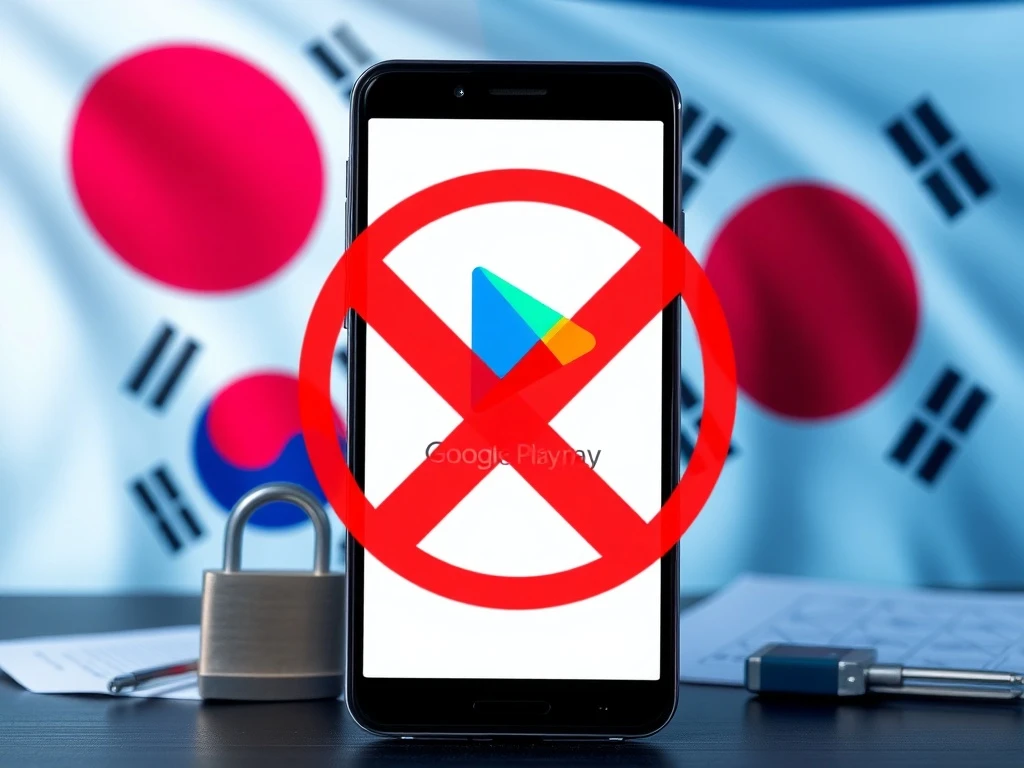

SEOUL, South Korea – January 2025 marks a pivotal moment for cryptocurrency accessibility in one of Asia’s most dynamic digital asset markets as Google Play implements stringent new requirements that could effectively ban unregistered offshore exchanges from serving South Korean users. This regulatory enforcement, requiring proof of Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) registration acceptance, represents a significant escalation in South Korea’s ongoing efforts to bring cryptocurrency exchanges under formal financial oversight while protecting domestic investors from potential risks associated with unregulated platforms.
Google Play Crypto Ban Reshapes South Korea’s Digital Asset Landscape
Google’s updated policy, effective January 28, 2025, fundamentally alters how cryptocurrency exchanges and custodial wallet providers can operate within South Korea’s digital ecosystem. The technology giant now mandates that developers upload documentation proving their Virtual Asset Service Provider (VASP) registration with the country’s Financial Intelligence Unit has been formally accepted. Consequently, applications failing to meet this requirement face potential blocking within South Korea, preventing new downloads and potentially disrupting existing user access over time.
This development follows Google Play’s global cryptocurrency policy update from August 14, 2025, which established a framework requiring exchanges and custodial wallet providers to meet specific jurisdictional licensing and regulatory standards. In the United States, developers must register with regulators like the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). Meanwhile, European Union operators must qualify as licensed crypto-asset service providers. South Korea’s implementation represents a particularly stringent application of this global policy, given the country’s comprehensive regulatory requirements for cryptocurrency businesses.
FIU Registration Presents Substantial Compliance Challenges
South Korea’s FIU registration process presents formidable barriers for offshore cryptocurrency exchanges seeking to serve Korean users legally. The comprehensive requirements include:
- Local Legal Entity Establishment: Companies must establish a formal corporate presence within South Korea
- Anti-Money Laundering Systems: Implementation of robust AML frameworks meeting Korean standards
- On-Site Inspections: Regulatory authorities conduct thorough operational examinations
- ISMS Certification: Obtaining Information Security Management System certification
These requirements collectively create what industry analysts describe as one of the most demanding regulatory environments for cryptocurrency exchanges globally. The process typically requires substantial financial investment, operational restructuring, and extended timeframes for completion. For many offshore exchanges, these hurdles have proven insurmountable, leading to continued operation without formal registration until Google’s policy change forced compliance.
Major Exchanges Face Immediate Operational Disruption
According to reporting from South Korean media outlet News1, the policy change particularly impacts major international cryptocurrency exchanges including Binance and OKX. While Binance maintains a 10% stake in local exchange Gopax, it lacks an official local entity in South Korea. Similarly, OKX previously faced allegations of operating as an unregistered cryptocurrency exchange within the country. A Binance spokesperson acknowledged awareness of the new policy while noting its broad impact across the cryptocurrency application ecosystem.
The spokesperson explained that users performing device changes, factory resets, application uninstalls, or major operating system updates requiring reinstallation “may temporarily be unable to re-download” their application from Google Play following policy implementation. Binance confirmed active engagement with Google seeking constructive resolution while reaffirming commitment to providing secure, reliable, and compliant services worldwide. OKX declined to comment on the regulatory development.
Contrasting Regulatory Approaches Within South Korea
Google Play’s enforcement arrives alongside South Korea’s advancement of separate regulatory initiatives focused on blockchain technology integration within capital markets. The National Assembly recently passed amendments to the Electronic Securities Act and Capital Markets Act, formally introducing tokenized securities and allowing regulated distribution of investment contract securities. This framework supports blockchain-based issuance and settlement within existing securities regimes while treating distributed ledger technology-issued securities as traditional financial instruments subject to standard disclosure, licensing, and investor-protection mandates.
This dual-track regulatory approach reflects South Korea’s nuanced stance toward digital assets: encouraging technological innovation and institutional adoption through clear frameworks while simultaneously protecting retail investors through stringent exchange regulations. The contrast between tightened application access and expanded tokenization opportunities highlights the government’s differentiated treatment of cryptocurrency trading platforms versus blockchain infrastructure development.
Historical Context of South Korean Cryptocurrency Regulation
South Korea’s current regulatory stance emerges from years of evolving cryptocurrency policy development. Following the 2017 cryptocurrency boom, authorities implemented real-name account requirements mandating bank partnerships for exchanges. The 2021 Specific Financial Information Act established the VASP registration framework now enforced through Google’s policy. Recent months have seen increased regulatory scrutiny, including discussions about pre-emptive cryptocurrency account freezes to prevent illicit activities.
This regulatory evolution reflects broader global trends toward cryptocurrency exchange oversight while maintaining South Korea’s distinctive approach emphasizing consumer protection and financial system integrity. The country’s high cryptocurrency adoption rates among retail investors have consistently driven regulatory attention to potential risks including market manipulation, fraud, and inadequate investor safeguards.
Global Implications of Platform-Enforced Compliance
Google’s policy implementation represents a significant development in global cryptocurrency regulation enforcement through technology platforms rather than direct government action. By leveraging its control over application distribution, Google effectively enforces South Korean regulatory requirements at the platform level, creating compliance mechanisms that transcend traditional jurisdictional boundaries. This approach potentially establishes precedents for other jurisdictions seeking to regulate offshore cryptocurrency exchanges serving domestic users.
The table below illustrates key differences between direct regulatory enforcement and platform-mediated compliance:
| Enforcement Method | Mechanism | Effectiveness | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Regulatory Action | Government investigations, penalties, legal proceedings | Comprehensive but resource-intensive | Jurisdictional boundaries, enforcement challenges |
| Platform-Mediated Compliance | Application store requirements, distribution controls | Immediate, scalable impact | Platform dependency, workaround possibilities |
This development raises important questions about the appropriate role of technology platforms in regulatory enforcement and the potential for similar approaches in other jurisdictions with stringent cryptocurrency regulations.
Industry Response and Adaptation Strategies
Cryptocurrency exchanges facing potential exclusion from South Korea’s Google Play marketplace must develop strategic responses to maintain market presence. Potential adaptation strategies include pursuing formal FIU registration despite substantial requirements, establishing partnerships with registered local exchanges, developing web-based platforms circumventing application store distribution, or potentially exiting the South Korean market entirely. Each approach presents distinct challenges and opportunities requiring careful consideration of regulatory compliance, operational feasibility, and market positioning.
Industry observers note that exchanges with existing regulatory compliance infrastructure in multiple jurisdictions may possess advantages in navigating South Korea’s requirements. Conversely, platforms with limited compliance resources or operating models incompatible with stringent regulations face difficult decisions about market participation. The evolving situation demonstrates how platform-level enforcement can dramatically reshape competitive dynamics within regulated cryptocurrency markets.
Consumer Impact and Market Consequences
South Korean cryptocurrency users face immediate practical consequences from Google’s policy implementation. While existing application installations may continue functioning temporarily, users requiring reinstallation face potential access disruption. This situation creates uncertainty for investors holding assets on potentially affected exchanges and may accelerate asset transfers to registered domestic platforms. Market analysts anticipate potential liquidity impacts on affected exchanges and possible price volatility for assets with significant South Korean trading volumes.
Longer-term consequences may include reduced accessibility to international cryptocurrency exchanges, potentially limiting product diversity and competitive pricing for South Korean users. However, registered domestic exchanges may experience increased trading volumes and user growth as alternatives to restricted international platforms. This regulatory development ultimately tests the balance between consumer protection and market accessibility within South Korea’s evolving digital asset ecosystem.
Conclusion
South Korea’s Google Play crypto ban represents a watershed moment in cryptocurrency regulation enforcement, demonstrating how technology platforms can implement jurisdictional requirements with immediate, tangible effects. The requirement for FIU registration acceptance documentation creates critical compliance hurdles for offshore exchanges including Binance and OKX while potentially reshaping South Korea’s digital asset landscape. This development occurs alongside progressive tokenization framework approvals, highlighting the country’s nuanced regulatory approach distinguishing between cryptocurrency trading platforms and blockchain infrastructure. As global cryptocurrency regulation continues evolving, South Korea’s platform-mediated enforcement model may establish important precedents for other jurisdictions seeking to regulate digital asset access while balancing innovation, consumer protection, and market development objectives.
FAQs
Q1: What exactly does Google’s new policy require for crypto apps in South Korea?
Google now requires cryptocurrency exchange and custodial wallet applications listed on Google Play in South Korea to upload documentation proving their Virtual Asset Service Provider registration with the country’s Financial Intelligence Unit has been formally accepted. Applications failing to meet this requirement may be blocked within South Korea.
Q2: Which cryptocurrency exchanges are most affected by this policy change?
Major international exchanges including Binance and OKX face significant impacts since they currently lack formal FIU registration in South Korea. While Binance has a stake in local exchange Gopax, it doesn’t maintain an official local entity. OKX has previously faced allegations of operating as an unregistered exchange in the country.
Q3: Can South Korean users still access affected exchanges through other methods?
Users with existing application installations may continue accessing exchanges temporarily, but those requiring reinstallation due to device changes, factory resets, or operating system updates may face access disruption. Alternative access methods might include web-based platforms or third-party application stores, though these may present security concerns or usability limitations.
Q4: How does this development relate to South Korea’s broader cryptocurrency regulatory approach?
The Google Play enforcement occurs alongside progressive regulatory developments including tokenized securities framework approvals, reflecting South Korea’s dual-track approach: encouraging blockchain innovation through clear frameworks while protecting retail investors through stringent exchange regulations and consumer safeguards.
Q5: What are the potential long-term consequences for South Korea’s cryptocurrency market?
Long-term consequences may include reduced accessibility to international exchanges, potential consolidation around registered domestic platforms, possible impacts on market liquidity and competition, and accelerated regulatory compliance across the cryptocurrency industry serving South Korean users.