Bitcoin Mining Difficulty Plummets 11% in Stunning Network Adjustment – Largest Drop Since China’s 2021 Ban

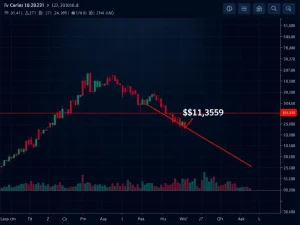
The Bitcoin network just experienced its most significant mining difficulty adjustment in over three years, with an 11% downward shift marking the largest single drop since China’s sweeping 2021 mining ban. This dramatic network recalibration coincides with notable commentary from Bitwise Chief Investment Officer Matt Hougan, who recently suggested Bitcoin’s price may avoid repeating the severe 77% drawdowns seen in previous cycles. The simultaneous occurrence of these two developments provides crucial insights into Bitcoin’s current network health and future price trajectory.
Understanding Bitcoin’s 11% Mining Difficulty Adjustment
Bitcoin’s mining difficulty automatically adjusts approximately every two weeks to maintain a consistent 10-minute block time. The recent 11% decrease represents the network’s response to reduced computational power, technically known as hash rate. This adjustment mechanism ensures Bitcoin remains decentralized and secure regardless of miner participation levels. Network analysts immediately recognized the significance of this drop, comparing it directly to the aftermath of China’s 2021 prohibition when difficulty plunged approximately 28%.
Several factors contributed to this substantial difficulty reduction. First, seasonal energy price fluctuations in key mining regions like Texas and Kazakhstan forced some operations to temporarily scale back. Second, older mining equipment became economically unviable following Bitcoin’s recent price consolidation. Third, some miners likely redirected resources toward alternative proof-of-work cryptocurrencies offering temporarily higher margins. The network’s response demonstrates Bitcoin’s remarkable resilience and self-correcting design principles.
Historical Context of Major Difficulty Adjustments
Bitcoin has experienced only a handful of double-digit difficulty reductions throughout its history. The table below illustrates the most significant adjustments:
| Date | Difficulty Change | Primary Catalyst |
|---|---|---|
| July 2021 | -28% | China’s mining ban |
| March 2020 | -16% | COVID-19 market crash |
| November 2022 | -7% | FTX collapse aftermath |
| Current Adjustment | -11% | Energy costs & equipment cycles |
These historical comparisons reveal important patterns. Major difficulty reductions typically follow significant external events affecting miner economics. However, the current adjustment appears more organic, resulting from normal market forces rather than regulatory shocks. This distinction matters greatly for assessing network health and future recovery prospects.
Bitwise CIO’s Price Stability Analysis
Separately, Bitwise Chief Investment Officer Matt Hougan recently addressed Bitcoin’s price volatility concerns. He specifically noted that Bitcoin may not experience another 77% drawdown similar to previous cycles. Hougan based this assessment on several structural changes within the cryptocurrency ecosystem. His analysis considers improved market infrastructure, institutional participation, and regulatory clarity developments. These factors collectively contribute to potentially reduced volatility moving forward.
Hougan’s commentary references Bitcoin’s historical drawdown patterns. Following the 2017 peak, Bitcoin declined approximately 83% over the subsequent year. Similarly, the 2021 peak preceded a 77% decrease. However, current market conditions differ substantially from previous cycles. The introduction of spot Bitcoin ETFs created new demand channels from traditional investors. Meanwhile, improved custody solutions and regulatory frameworks reduced operational risks for institutional participants.
The Bitwise executive highlighted several key indicators supporting his stability thesis:
- Institutional adoption: Major financial institutions now offer cryptocurrency services
- Regulatory progress: Clearer frameworks in major markets like the EU and UK
- Market maturity: Reduced leverage and improved risk management practices
- Infrastructure development: Robust trading, custody, and settlement systems
Network Fundamentals Versus Price Speculation
The relationship between mining difficulty adjustments and price movements remains complex. Historically, significant difficulty reductions often preceded substantial price rallies. Following China’s 2021 mining ban and subsequent difficulty drop, Bitcoin’s price increased approximately 70% over the next four months. This pattern emerged because difficulty adjustments frequently signal miner capitulation moments, which traditional analysts consider contrarian indicators.
Current network data reveals additional encouraging signs. Despite the difficulty reduction, Bitcoin’s hash rate remains near all-time highs, excluding recent fluctuations. This suggests the network maintains robust security even during temporary adjustments. Furthermore, miner revenue metrics show improving trends as operational efficiencies offset reduced participation. These fundamental improvements support Hougan’s price stability arguments by demonstrating network resilience.
Implications for Bitcoin Miners and Investors
The 11% difficulty reduction provides immediate relief for remaining miners. With lower competition for block rewards, operational margins improve for efficient mining operations. This adjustment particularly benefits miners with:
- Access to low-cost, sustainable energy sources
- Modern mining equipment with superior efficiency ratings
- Strategic geographic diversification across multiple regions
- Hedging strategies against energy price volatility
For investors, the difficulty adjustment and Hougan’s analysis together suggest several important considerations. First, network security remains strong despite temporary hash rate fluctuations. Second, miner economics continue evolving toward greater sustainability. Third, institutional perspectives increasingly emphasize Bitcoin’s maturation beyond extreme volatility patterns. These developments collectively support a more nuanced investment thesis focused on long-term fundamentals rather than short-term speculation.
Market analysts note additional positive indicators. Bitcoin’s network activity shows consistent transaction volumes despite price consolidation. Meanwhile, address growth metrics indicate steady adoption beyond speculative trading. These on-chain signals complement the mining difficulty narrative by painting a comprehensive picture of network health. When combined with Hougan’s institutional perspective, they suggest Bitcoin’s ecosystem continues maturing across multiple dimensions.
The Global Mining Landscape Evolution
Since China’s 2021 mining ban, Bitcoin mining has undergone dramatic geographical redistribution. The United States emerged as the dominant mining hub, currently representing approximately 38% of global hash rate. Other regions including Kazakhstan, Russia, and Canada also gained significant market share. This geographical diversification strengthened network resilience against regional regulatory changes or energy disruptions.
The mining industry simultaneously advanced its environmental sustainability initiatives. Recent estimates suggest renewable energy sources now power over 50% of Bitcoin mining operations. This progress addresses previous environmental concerns while improving mining’s long-term economic viability. Furthermore, innovative miners developed demand response programs that support electrical grid stability during peak usage periods. These developments demonstrate mining’s evolving role within broader energy ecosystems.
Conclusion
Bitcoin’s 11% mining difficulty adjustment represents a significant network event with important implications for miners and investors. This reduction, the largest since China’s 2021 ban, reflects normal market forces rather than systemic shocks. When analyzed alongside Bitwise CIO Matt Hougan’s price stability commentary, these developments suggest Bitcoin’s ecosystem continues maturing. The network demonstrates remarkable resilience through its automatic adjustment mechanisms, while institutional perspectives increasingly recognize reduced volatility potential. Together, these factors indicate Bitcoin’s ongoing evolution toward greater network stability and market maturity, potentially supporting more sustainable growth patterns in future cycles.
FAQs
Q1: What causes Bitcoin’s mining difficulty to adjust?
Bitcoin’s protocol automatically adjusts mining difficulty approximately every 2,016 blocks (about two weeks) to maintain a consistent 10-minute block time. The adjustment responds to changes in total network computational power, ensuring security and predictability regardless of miner participation levels.
Q2: How does the current 11% difficulty reduction compare to historical adjustments?
The current 11% reduction represents the largest single adjustment since July 2021, when China’s mining ban caused a 28% difficulty drop. Other significant reductions include March 2020’s 16% decrease following COVID-19 market turmoil and November 2022’s 7% reduction after the FTX collapse.
Q3: What does Bitwise CIO mean by Bitcoin avoiding 77% drawdowns?
Matt Hougan suggests structural changes in Bitcoin’s market—including institutional adoption, improved infrastructure, and regulatory progress—may prevent the extreme 77%+ price declines seen after previous cycle peaks. He believes these developments support potentially reduced volatility moving forward.
Q4: How does mining difficulty affect Bitcoin’s price?
Historically, significant difficulty reductions often preceded price rallies as they signaled miner capitulation moments. However, the relationship remains complex with multiple influencing factors. Current analysis suggests difficulty adjustments primarily reflect miner economics rather than directly causing price movements.
Q5: What are the implications for Bitcoin miners after this adjustment?
The difficulty reduction improves profitability for remaining miners by decreasing competition for block rewards. Efficient operations with modern equipment and low-cost energy benefit most. The adjustment may also accelerate the retirement of outdated mining hardware, potentially improving network efficiency long-term.